A computer system is divided into two categories: Hardware and Software. Hardware refers to the physical and visible components of the system such as a monitor, CPU, keyboard and mouse. Software, on the other hand, refers to a set of instructions which enable the hardware to perform a specific set of tasks. The software must be installed in the hardware to function properly and similarly, the hardware must be present for the tasks to be performed. Both are interdependent, yet they are also different from each other.
Differences between Hardware and Software
| Hardware |
Software |
| Hardware is further divided into four main categories:
|
Software is further divided into two main categories:
|
| Developed using electronic and other materials | Developed writing using instructions using a programming language |
| When damaged, it can be replaced with a new component | When damaged it can be installed once more using a backup copy |
| Hardware is physical in nature and hence one can touch and see hardware | The software cannot be physically touched but still can be used and seen |
| Hardware cannot be infected by Viruses | The software can be infected by Viruses |
| Hardware will physically wear out over time | Software does not wear out but it can be affected by bugs and glitches |
| An example of Hardware is hard drives, monitors, CPU, scanners, printers etc. | An example of software is Windows 10, Adobe Photoshop, Google Chrome etc. |
A computer device is made up of various elements which help in its effective functioning and processing. There are five basic components of the computer which help in making this processing of data easier and convenient.
In this article, we shall discuss the basic computer components along with their functions. Also, for candidates preparing Computer Knowledge for upcoming competitive exams, sample questions based on this concept have been given further below in this article.
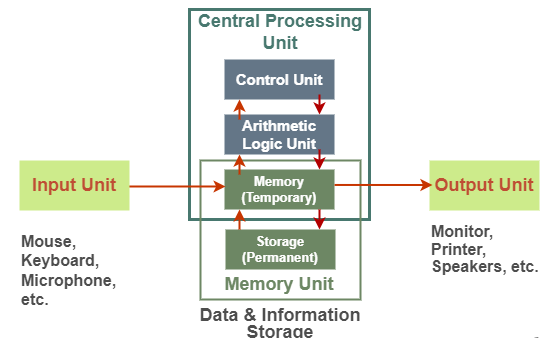
By definition, components of a computer system are the primary elements which make the functioning of an electronic device smooth and faster. There are five basic components which include:
- Input Unit
- Output Unit
- Memory Unit
- Control Unit
- Arithmetical and Logical Unit
Types of Computer
There are majorly 4 types of computers which have been described briefly below. Candidates must know about the different types of computers with respect to the upcoming competitive exams:
- Super Computer – The computers which are used to process a huge amount of data at once are called Supercomputers. They are mostly used in scientific and engineering operations where the processing is complex. They are expensive and complicated to work. For example – The computers used by NASA to launch space shuttles.
- Mainframe Computer – Computers designed to be used in large firms and organisations where a lot of people have to work on the same database are called mainframe computers. They are almost equally as expensive as Supercomputers and are the fastest working computers at present. They are mostly used in Banks.
- Workstation – Usually a single user system is called a work station. The RAM for such systems is more, and the processors are quite fast. They are mostly used by an individual and can be used for multiple purposes.
- Microcomputer – Designed for personal use only. This type of computers can easily be moved from one place to the other. They have a personal storage area, input & output unit and a Central Processing Unit. Examples for microcomputer are desktop, laptop, mobile phone, tablets, etc.
A storage device for a computer enables its user to store and safely access the data and applications on a computer device. Knowing and learning about these computer storage devices is necessary as it works as one of the core components of the system.
Types of Computer Storage
The computer storage unit is divided into three parts. Given below are details about the three types of computer storage:
- Primary Storage: This is the direct memory which is accessible to the Central Processing Unit (CPU).
- This is also known as the main memory and is volatile.
- This is temporary. As soon as the device turns off or is rebooted, the memory is erased
- It is smaller in size
- Primary storage comprises only of Internal memory
- Examples of primary storage include RAM, cache memory, etc.
- Secondary Storage: This type of storage does not have direct accessibility to the Central Processing Unit.
- The input and output channels are used to connect such storage devices to the computer, as they are mainly external
- It is non-volatile and larger storage capacity in comparison to primary storage
- This type of storage is permanent until removed by an external factor
- It comprises of both internal and external memory
- Examples of secondary storage are USB drives, floppy disks, etc.
- Tertiary Memory: This type of storage is generally not considered to be important and is generally not a part of personal computers.
- It involves mounting and unmounting of mass storage data which is removable from a computer device
- This type of storage holds robotic functions
- It does not always require human intervention and can function automatically
List of Computer Storage Devices
There are four types of devices in which computer data can be stored. Discussed below are the same in detail.
Magnetic Storage Devices
The most commonly used storage devices in today’s time are magnetic storage devices. These are affordable and easily accessible. A large amount of data can be stored in these through magnetised mediums.
A magnetic field is created when the device is attached to the computer and with the help of the two magnetic polarities, the device is able to read the binary language and store the information. Given below are the examples of magnetic storage devices.
- Floppy Disk – Also known as a floppy diskette, it is a removable storage device which is in the shape of a square and comprises magnetic elements. When placed in the disk reader of the computer device, it spins around and can store information. Lately, these floppy disks have been replaced with CDs, DVDs and USB drives
- Hard Drive – This primary storage device is directly attached to the motherboard’s disk controller. It is integral storage space as it is required to install any new program or application to the device. Software programs, images, videos, etc. can all be saved in a hard drive and hard drives with storage space in terabytes are also easily available now
- Zip Disk – Introduced by Iomega, is a removable storage device which was initially released with a storage space of 100 MB which was later increased to 250 and then finally 750 MB
- Magnetic Strip – A magnetic strip is attached in the device comprising digital data. The most suitable example for this is a debit card which has a strip placed on one of its sides which stores the digital data.
Optical Storage Devices
Such devices used lasers and lights to detect and store data. They are cheaper in comparison to USB drives and can store more data. Discussed below are a few commonly used optical storage devices.
- CD-ROM – This stands for Compact Disc – Read-Only Memory and is an external device which can store and read data in the form of audio or software data
- Blu-Ray Disc – Introduced in 2006, Blu-ray disk was backup up by major IT and computer companies. It can store up to 25 GB data in a single-layer disc and 50 GB data in a dual-layer disc
- DVD – Digital Versatile Disc is another type of optical storage device. It can be readable, recordable, and rewritable. Recordings can be done in such devices and then can be attached to the system
- CD-R – It is a readable Compact Disc which uses photosensitive organic dye to record data and store it. They are a low-cost replacement for storing software and applications.
Flash Memory Devices
These storage devices have now replaced both magnetic and optical storage devices. They are easy to use, portable and easily available and accessible. They have become a cheaper and more convenient option to store data.
Discussed below are the major flash memory devices which are being commonly used by the people nowadays.
- USB Drive – Also, known as a pen drive, this storage device is small in size and is portable and ranges between storage space of 2 GB to 1 TB. It comprises an integrated circuit which allows it to store data and also replace it
- Memory Card – Usually attached with smaller electronic and computerised devices like mobile phones or digital camera, a memory card can be used to store images, videos and audios and is compatible and small in size
- Memory Stick – Originally launched by Sony, a memory stick can store more data and is easy and quick to transfer data using this storage device. Later on, various other versions of memory stock were also released
- SD Card – Known as Secure Digital Card, it is used in various electronic devices to store data and is available in mini and micro sizes. Generally, computers have a separate slot to insert an SD card. In case they do not have one, separate USBs are available in which these cards can be inserted and then connected to the computer.